Professor Declan Gilheany - Fourth Year Projects 2015/16
1. Catalytic Asymmetric Grignard reaction. In recent decades, catalytic asymmetric synthesis has become one of the fastest growing fields of organic chemistry, subject of the Nobel prize in 2001. Despite huge interest in the subject, a general asymmetric method of forming C-C bonds has not yet been developed and is still a major challenge for organic chemists.
We have recently make a breakthrough towards the desirable process shown in Scheme 1 for M=Mg (i.e. the Grignard reaction - one of the most common methods of CC bond formation) and have achieved selectivities up to 95% ee in certain cases. This has been notified to NovaUCD and a preliminary patent has been lodged. The Honours project will seek to improve the process, both by expansion of the types of substrates and, especially, the catalysis aspects. You will be making (by organic synthesis, 3-4 steps) various ligands for magnesium, trying them in the reaction and testing the alcohols produced by chiral HPLC. Some insight into the commercialisation process will also be gained in the project.
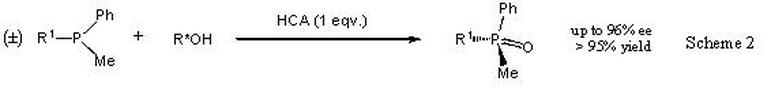
2. P-stereogenic phosphorus compounds. Creating stereochemistry at phosphorus is notoriously difficult. Some years ago, we made a scientific breakthrough[i] that provided a route to the sub-class of tertiary phosphine oxides, Scheme 2.
We recently published how it works along with an improved and easy-to-run version.[ii] There are 3 related Honours projects:
A: Expansion of the substrate scope and selectivity studies. This involves substantial synthetic work under air- and moisture-free conditions and analyses by chiral HPLC. This could also be combined with project 3A below.
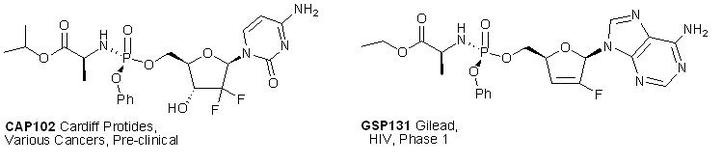
B: P-Stereogenic components of ProTide drugs. Certain well-known useful drugs such as Zovirax (cold sores) and AZT (HIV) are classed as nucleosides. The ProTide drugs are nucleosides carrying an extra phosphorus-containing piece, which enables their activation to the active nucleotide. Unfortunately, the direct synthesis of this piece is nearly impossible at present because it is P-stereogenic with some attachments via atoms other than carbon. Examples are CAP102 and GS9131.
We found that our new method (Scheme 2) can be applied to ProTide model compounds (with nitrogen attached to P) and we want to explore this further. Again the project involves synthetic work under air- and moisture-free conditions with HPLC analysis. Note that the project is not to make drugs, rather explore a route towards the synthesis of ProTide drug candidates.
3. Theoretical Calculations.
A: In Phosphorus Chemistry Now that we think we understand Scheme 2, it is amenable to exploration by such methods. The project combines computer-based work (mainly on a PC) with laboratory work. But you would have to be comfortable to engage with advanced techniques of chemistry computation (e.g. DFT calculations).
B: With Dr. Goar Sanchez (School of Chemistry). If you are comfortable with theoretical and computational chemistry, there is also an opportunity to do a purely computer-based project. I have a collaboration with Dr. Sanchez who does very high level calculations, please speak to me about this if you are interested.
A: In Phosphorus Chemistry Now that we think we understand Scheme 2, it is amenable to exploration by such methods. The project combines computer-based work (mainly on a PC) with laboratory work. But you would have to be comfortable to engage with advanced techniques of chemistry computation (e.g. DFT calculations).
B: With Dr. Goar Sanchez (School of Chemistry). If you are comfortable with theoretical and computational chemistry, there is also an opportunity to do a purely computer-based project. I have a collaboration with Dr. Sanchez who does very high level calculations, please speak to me about this if you are interested.
References
(i) P-Stereogenic Phosphorus Compounds. Asymmetric Oxidation of Phosphines under Appel Conditions. E. Bergin, C.T.
O'Connor, S.B. Robinson, E.M. McGarrigle, C.P. O'Mahony and D.G. Gilheany, Journal of the American Chemical Society,
2007, 129, 9566.
(ii) Turning Regioselectivity into Stereoselectivity: Efficient Dual Resolution of P-Stereogenic Phosphine Oxides via Bifurcation in
the Reactivity of a Common Intermediate. K. Nikitin, K. V. Rajendran, H. Müller-Bunz and D. G. Gilheany, Angewandte
Chemie International Edition, 2014, 53, 1906.
(i) P-Stereogenic Phosphorus Compounds. Asymmetric Oxidation of Phosphines under Appel Conditions. E. Bergin, C.T.
O'Connor, S.B. Robinson, E.M. McGarrigle, C.P. O'Mahony and D.G. Gilheany, Journal of the American Chemical Society,
2007, 129, 9566.
(ii) Turning Regioselectivity into Stereoselectivity: Efficient Dual Resolution of P-Stereogenic Phosphine Oxides via Bifurcation in
the Reactivity of a Common Intermediate. K. Nikitin, K. V. Rajendran, H. Müller-Bunz and D. G. Gilheany, Angewandte
Chemie International Edition, 2014, 53, 1906.